Animal production practices have evolved over the years to meet the food protein needs of the growing human population. Some farms became very large, and used modern production practices to push food animal growth rates to their maximum.
Disease prevention, husbandry, genetics and nutrition have greatly improved the efficiency of many food animal production facilities.
To some extent, the industrialization of animal production was made possible by the availability of antibiotics for livestock and poultry. Although antibiotic usage has clearly benefited the animal industry and helped provide affordable animal protein to the growing human population, the use of antibiotics in food production also contributed to the emergence and spread of AMR.
Along with antibiotics used for human medicine, antibiotic use for animal treatment, prophylaxis and growth promotion exerts an inestimable amount of selective pressure toward the emergence and propagation of resistant bacterial strains.

Health Implications
- Infections: Infections caused by resistant bacteria are more difficult to treat, leading to longer illness durations, higher medical costs, and increased mortality. Common infections include urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections.
- Treatment Challenges: The effectiveness of antibiotics is reduced, necessitating the use of more potent and often more toxic drugs. This can lead to adverse side effects and complicate treatment protocols.
- Increased Burden on Healthcare Systems: The rise in resistant infections places a significant burden on healthcare systems. More resources are required for diagnosis, treatment, and longer hospital stays, straining already limited healthcare infrastructures.
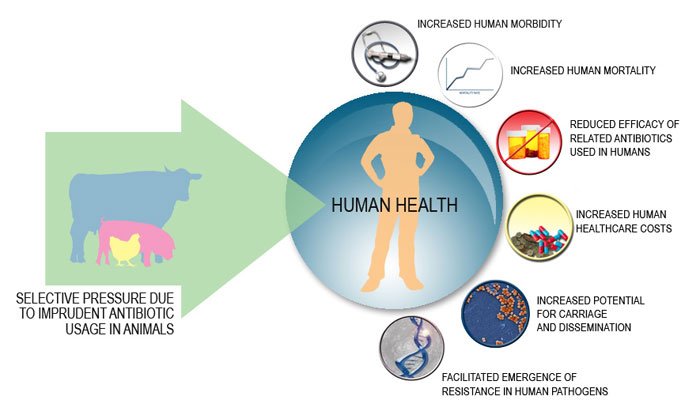
Animals can serve as mediators, reservoirs and disseminators of resistant bacterial strains and/or AMR genes.
Consequently, imprudent use of antimicrobials in animals may eventually result in increased human morbidity, increased human mortality, reduced efficacy of related antibiotics used for human medicine, increased healthcare costs, increased potential for carriage and dissemination of pathogens within human populations and facilitated emergence of resistant human pathogens.




